Also in the news...
France: providing services and travelling for business
Guidance for UK businesses on rules for selling services to France.
Living in the USA
Information about moving to, living or retiring in the USA Ė including visas, working, healthcare and driving.
Trade with Liechtenstein
How you import from and export to Liechtenstein
UK trade with the United States: Impact of tariffs on imports and exports of goods
A closer look at the goods the UK trades with the United States in the context of trade tariffs.
Simplified rates for bringing personal goods into the UK
Find out about the simplified rates of customs and excise duty used when you declare your personal goods online.
Iranís Risk Rating has upgraded to 5
Iran's rating in the country risk classifications of the Participants to the Arrangement on Officially Supported Export Credits (CRE), has upgraded from 6 to 5 by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD).
After the last upgrade in Iranís rating in the country risk on June 2016, from 7 to 6, the OECD announced following its last meeting on Friday that Iranís risk rating has moved from 6 to 5.
According to OECD, the country risk classifications are meant toreflect country transfer and convertibility risk (Under the Participantsí system, country risk encompasses transfer and convertibility risk (i.e. the risk a government imposes capital or exchange controls that prevent an entity from converting local currency into foreign currency and/or transferring funds to creditors located outside the country).
Arash Shahraini, deputy head of Export Guarantee Fund of Iran, said during a telephone interview that ďThe upgrade was indeed a positive signal from the Europeans and a further indication of their interest to continue engaging with Iran within the framework of the nuclear deal,Ē
After the JCPOA (Nuclear Deal) between Iran and the P5+1 in 2015 and partial relief from International sanctions, Iran was expected the upgrade in risk rating in order to reduce the cost of attracting foreign finance and consequently increase the foreign exchange reserves.
This improvement is an important measure from OECD especially when US President, Donald Trump, tries to persuade Europeans to agree on imposing new sanctions against Iran.
According to the International Monetary Fundís report in February 2017, Iranís official reserves were projected at $123.5 billion in 2016 -17 and the total debt to GDP of the country stood at 2.2%, which was lowest in the world. Also, the global lender reported 12.5% economic growth in Iran as the highest in the world.
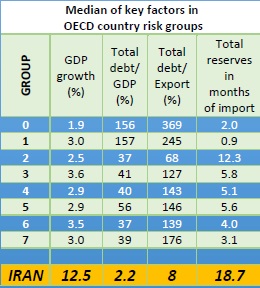
Iranís economic indicators compared with the average performance of countries in each risk classification, showing that in 2016, Iran has outperformed other countries, according to the EGFIís report. ďThere are other factors that have a bearing on the OECDís final assessment including political risks and a countryís history in settling its external debtsĒ, a senior EGFI officer said.
During the sanctions era, Iran wasnít able to settle its external debts due to the restrictions in its financial relations with other countries. However, after the JCPOA and partial elimination of sanctions, the Central Bank of Iran (CBI) repaid the countryís debts and signed several restructuring agreements within a year.
Some of the signed agreements between Iran and other countries after the nuclear deal, are as follows:
Two agreements with China Development Bank and CITICTrust which worth $25 billion, an agreement worth €5 billion with Italyís Invitalia Global Investment, A contract with Austriaís Oberbank worth €1 billion, €500 million deal with Denmark's Danske Bank and two agreements worth €13 billion with South Koreaís Exim Bank and K-Sure.
Iran and Non-OECD countries
The upgrade in Iranís risk classification will improve business relations between Iran and financial institutions in the OECD-member countries and will boost their intention to expand collaboration with Iran, what their non-OECD competitors are already doing.
Iran has exported $7.73 billion worth of non-oil goods to BRICS member countries (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa) during eight months in 2017 which shows 7.71% growth and comprises one-third of Iranís non-oil trade during this period. Since the nuclear deal was implemented, the BRICS countries have increasingly upgraded Iranís rating in their risk classifications.
Source: Financial Tribune
Shanda Consult is specialised in consultancy regarding project-based investments and as a partner in bringing together investors and investment projects.
For any consultation regarding your Iran-related business needs, please contact us.
Article supplied bt Shanda Consult
